2-dimentional Laser Displacement SensorsLS Series
Line beam for fast, accurate measuring of height and width
- Linearity of ±0.1% F.S.
- Sampling period of 0.5 ms (max. speed)
- 2-dimensional measurements at a significantly low cost


Various measurement functions
-
Height
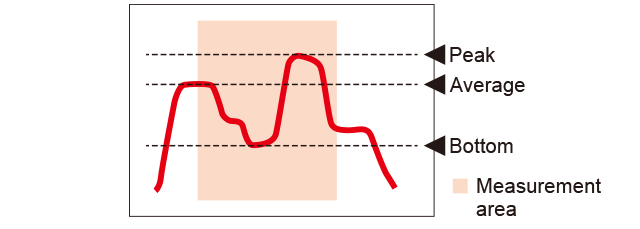
Average, peak, and bottom heights can be measured.
Average values, max. values, and min. values of a profile within an area are output. -
Position
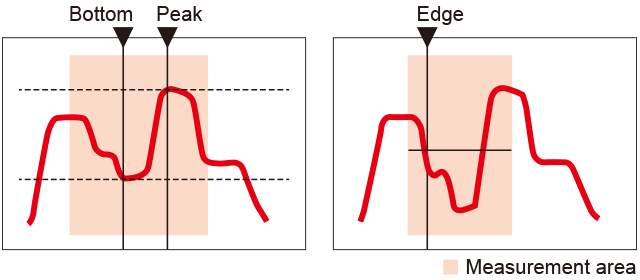
Peak, bottom, and edge positions can be measured.
-
Width
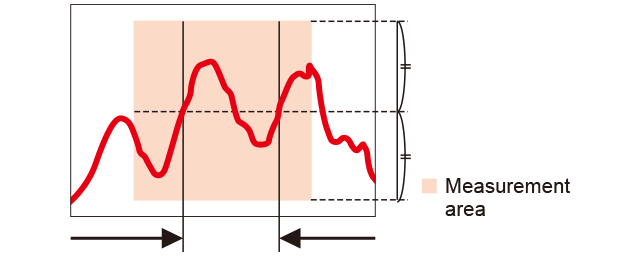
Groove and height difference widths can be measured. Profile widths are detected using the center position in the height direction of the area.
-
Edge count
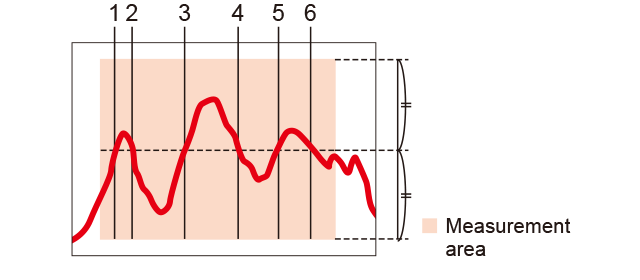
The number of times the center of the area's height is crossed is counted.
Use is also possible for pin counts, etc.
-
Tilt (°)
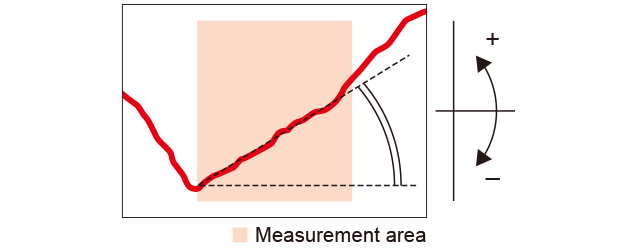
A straight line approximating the profile is created and its tilt is measured. (Unit: °) The angles of both sides of grooves and protrusions are measured and calculated.
-
Area (mm2)
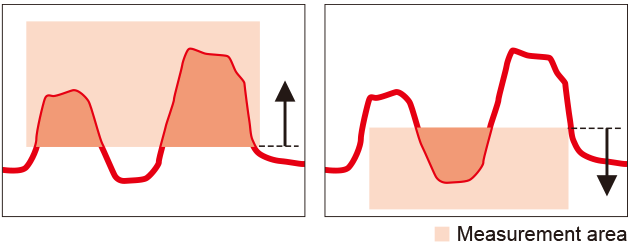
The area between an area and a profile is calculated
Measuring the “↑” portion reveals the cross-section of the protrusion, while the “↓” portion reveals the cross-section of the concave.
-
Line length
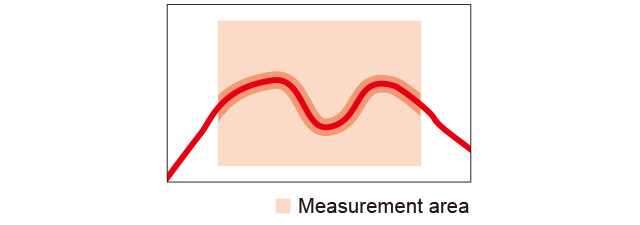
The profile length is measured. Because the same value will be achieved even if the position is changed, usage is possible without having to perform position corrections.
-
Diameter
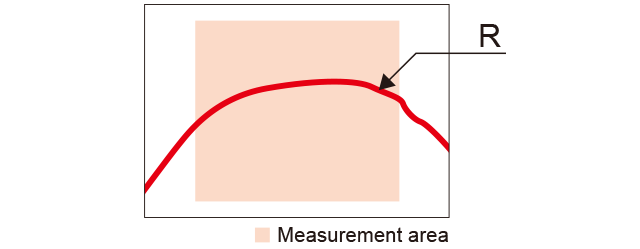
The diameter of the approximate bending line of the measured results is measured. This can be used for calculating the diameters cylinders, protrusions or grooves.
A wide-range of measurement variations using area calculations
-
▪ Example of height difference measurement
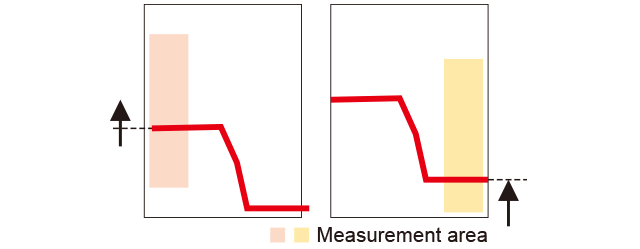
Height is measured at two areas (top and bottom surfaces) from which the height difference can be measured by subtracting. Small unevenness and variations can be ignored and it is possible to perform more stable measurements than with 1D displacement sensors.
-
▪ Example of angle measurement
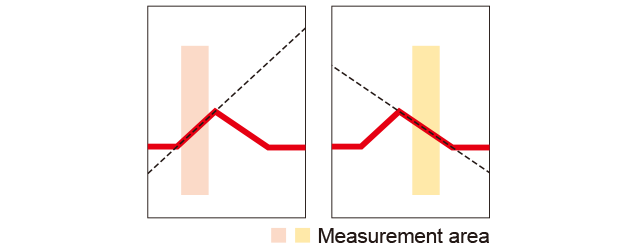
Tilting to the left or right is measured using two areas from which the angle can be measured by subtracting.
The external angles of both grooves and protrusions can be measured correctly.