Technical Guide for Displacement Sensors
1. Requirements to Be Confirmed
| Category | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Purposes | |
| Object | Color | Reflection rate, Transparency, Opaque, etc. |
| Dimensions | To fit within a measurement range | |
| Tilt | Measurement on a tilted surface could be unstable. | |
| Surface Condition | Measurement on a rough surface could be fluctuated. | |
| Accuracy | Repeat Accuracy, Resolution | |
| Linearity | ||
| Environment | Temperature | |
| Ambient Light | Caution is needed under direct sunlight or strong light. | |
| Production Line | Transfer Speed | |
| Tact Time | ||
| Interface | Input | for Trigger |
| Output | Control, Analog and Communication |
page top 
2. Selection Flow
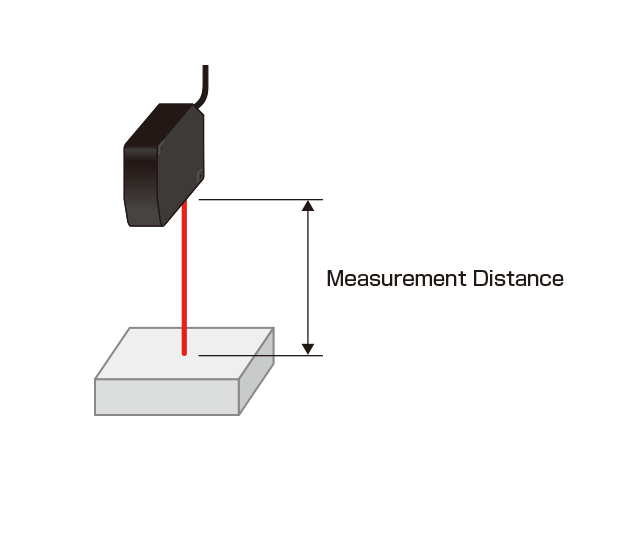
❶ Select a model for a measurement distance.
-
Select a model for an installation distance, measurement range and object dimensions.
-
❷ Select a model for object conditions.
-
Select a specular reflective model for transparent or specular object or a diffuse reflective model for others.
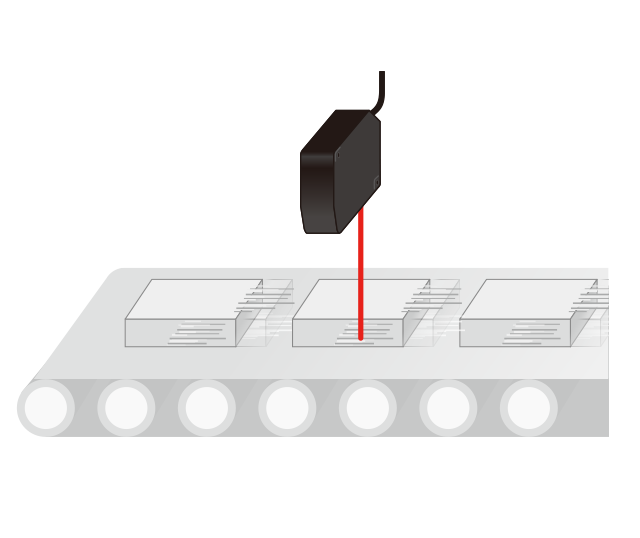
❸ Consider a required sampling period.
-
For measurement on a high-speed transfer line select a model that supports a short sampling period.
-
❹ Consider a required measurement accuracy.
-
Select a model to meet required measurement accuracy.
Compared with a required accuracy, 10 times of a sum of linearity and repeat accuracy is a guideline for selection.
As the moving resolution varies among objects, testing with actual samples is highly recommended.
〈Calculation of Linearity〉
Linearity = +/- percentage x full scale
〈Calculation Example〉
A Model with Linearity of +/- 0.1% and Full scale of +/- 20mm
= +/- 0.1% x +/- 20mm
= +/- 0.1% x 40mm
= +/- 0.04mm = 40μm
Shorter the distance between a laser displacement sensor and measurement object is, higher accuracy the measurement results will be.
If the required accuracy cannot be obtained, consider again a model in the same series with a shorter measurement range or a model in the higher series with a higher accuracy.
page top