Technical Guide for Photoelectric Sensors
1. What is Photoelectric Sensor
-
Photoelectric sensors detect presence of an object without contact, using light reflection.
They make an output signal according to an amount of received light that is reflected from a detection target.
They are mainly used to contribute to automation and labor-saving at manufacturing factories. 
page top 
2. Main Features
-

- Detection without contact
-

- Detection in long distance
-

- Detection of small objects
-

- Detection regardless of materials
-

- Fast response time
-

- Dirt on lens with liquid or dust
page top 
3. How to select a photoelectric sensor
| Purpose and condition | To be considered | Applicable sensors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection by detection | Positioning by detection of presence |
- Positioning accuracy - Easy installation |
- Through-beam - Laser - BGS |
| Small-object detection |
- Small spot sizes - Adjustable sensitivity |
- Fiber - Laser |
|
| Detection of fast-moving objects | - Short response time | - Fiber | |
| Transparent-object detection | - High-sensitivity/retro reflective | - Transparent-object detection | |
| Detection of surface unevenness | - Small hysteresis |
- Diffuse reflective - BGS - Displacement |
|
| Color mark detection |
- Colors of color mark, background and sensor light - Short response time |
- Color mark detection - Fiber |
|
| Color contrast detection | - High resolution | - Mark sensor | |
| Detection of less influenced by color differences | - High-resolution receiver element | - Laser BGS | |
| Selection by installation location | Small space | - Small sizes |
- Fiber - Miniature, Head-on/side-on |
| Installation on one side |
- Diffuse reflective, Limited diffuse reflective - BGS |
||
| Reflection from background | - Small hysteresis | - BGS | |
| Influence from ambient illuminance | Wider resistance against ambient illuminance | - Laser | |
| Robustness |
- Resin filled - Metal housing |
||
| Location with water | - High water resistance | - IP67, IP69K | |
page top 
4. Sensor structures
| Type | Detection method | Description | Popular models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Through-beam |
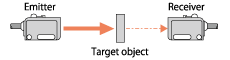
|
- Each of emitter and receiver units are used in a pair. - As an amount of received light is comparably larger, it is less influenced from dust in environment. |
Z4T-2500N ZT-L3000N |
| Retro reflective |
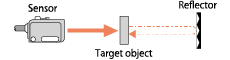
|
- A pair of sensor and reflector is used. - These require less installation space and wiring, compared with through-beam sensors. |
Z4R-400N ZR-L1000N |
| Diffuse reflective |

|
- A single unit of sensor detects light reflection from a detection object. - These require less installation space and wiring. |
Z4D-100N |
| Wide-angle diffuse reflective |
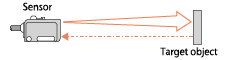
|
- A wider aperture angle is equipped to detect a small difference in received light amount. These are suitable to detect an object of transparent and with slit. | Z3D-W20N |
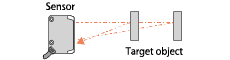
| Back Ground Suppression |
|
- A light receiving element of PSD or C-MOS is used to make an output upon detection at a preset distance. Detection of these models are less influenced from colors and materials of an object. |
BGS-HDL05T BGS-ZL10N Z4B-10N BGS-2V50 |
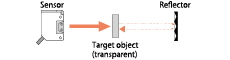
| Transparent-object detection |
|
- A pair of sensor unit with a low hysteresis and reflector detects a small difference in received light amount. These are suitable to detect a transparent object, such as a film and glass. |
DR-Q400TN ZR-QX200N KR-Q50NW KR-Q300NW |
| Separate amplifier |
|
- A combination of sensor unit and amplifier can be selected according to application requirements. - Various detection configurations can be set on an amplifier. |
D2SA-MN DSD-100 |
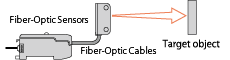
| Fiber-Optic Cables |
|
- An optical fiber is used to transfer light from and to an sensor. |
NF-DB01 NF-DF08 NF-TR01 NF-DC39 |
| Fiber-Optic Sensors |
|
- A combination of Fiber-Optic Cables and Fiber-Optic Sensors can be selected according to application requirements. - Small dimensions of Fiber-Optic Cables makes its installation possible in a small space. Combinations of various models can be made, even for detection of a color, height gap and liquid level. |
D4RF-T |
| Color mark detection |

|
- High resolution sensors can detect subtle color differences and color contrast. | DM-18TN |
page top 
5. Glossary of photoelectric sensors
| Term | Description | Term | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensing distance |
Through-beam The distance between an emitter and receiver. 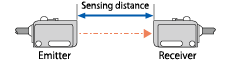
|
Light ON |
An output turns on, when a received light amount reaches a certain level.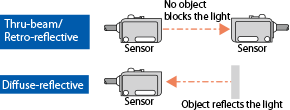
|
|
Retro reflective The distance between a sensor and reflector. 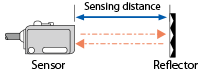
|
Dark ON |
An output turns on, when a received light amount is below a certain level.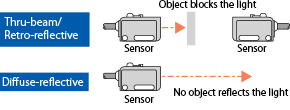
|
|
|
Diffuse reflective The distance between a sensor and standard detection object. 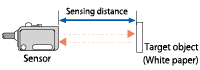
|
Laser off input | An external input can be used to stop light emittance of the sensor. | |
| Smallest detection object |
Smallest sizes of object that can be detected by a sensor.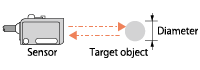
|
External input |
Output of a sensor can be made, according to status of an external input.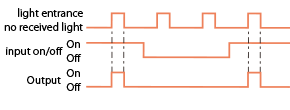
|
| Response time |
Time to turn on or off an output, according to presence of an object.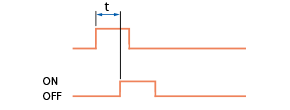
|
External Teaching |
Teach setting of a sensor can be triggered by an external input.
|
| Hysteresis |
A distance between a point that a reflective sensor makes an output on a standard detection object and, then, a point that it turns the output off. 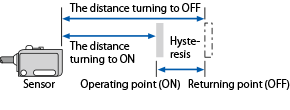
|
Off-delay timer |
An output is held for a preset time. The function can be combined with controller programs. 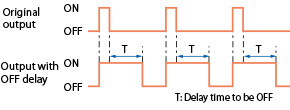
|
| Repeat accuracy |
A variation range in which a sensor performs detection.
|
page top 
6. Glossary of fiber sensors
| Term | Description | Term | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Array |
Fiber cores are aligned in a line to emit light in a flat beam. It is suitable to detect objects with unstable reflection, due to not fixed passages or uneven shapes. There are also Screen types of Fiber-Optic Cables in a similar structure. |
Limited diffuse reflective |
This Fiber-Optic Cables is used to make detection within a limited distance. Light axises of emitter and receiver are set at angles to make detection within their crossing area. 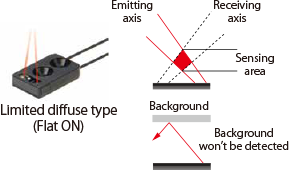
|
| Liquid level detection |
The Fiber-Optic Cables are used for liquid level control. There are contact types that detect a level by contact and pipe-installed types to be installed on a transparent pipe to make detection. |
Fine fiber |
Fiber cores with diameters of less than 0.5mm are called as a fine fiber. A thin light axis through fine fiber makes detection of a small object easy, but in a short detection distance. |
| Flexible |
A Fiber-Optic Cables that does not get broken, even when it is bent in a small radius. The R1 Fiber-Optic Cables can be bent to r1mm, R2 to r2mm. Although, in general, bending a Fiber-Optic Cables shortens its detection distance, the distances of flexible fibers are not influenced by bending. * To install a Fiber-Optic Cables on a moving part that repeatedly bends the fiber, bending-resistant Fiber-Optic Cables are recommended. |
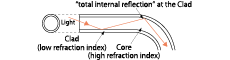
Core |
A part of fiber that transfers light is a core. The drawing below shows a diffuse Fiber-Optic Cables consists of an emitter core of φ0.5 and 9 receiver cores of φ0.25. 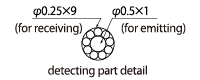
|
| Retro reflective | A Fiber-Optic Cables and reflector are installed on both sides to detect an object in between. | Side-on and side-view |
A Fiber-Optic Cables that its detection direction is to a side of the unit with an optical system installed on the side. With the Square units, it is called Side-On, and with the Sleeve units Side-View. 
|
| Aperture angle |
It is an angle of emitted and receiving light from a Fiber-Optic Cables. Generally Fiber-Optic Cables come with an aperture angle of 60˚, while narrow-view Fiber-Optic Cables with 2~5˚. 
|
Screen |
This comes with a lens to emit light in a flat beam. This is suitable to detect objects with unstable reflection, due to not fixed passages or uneven shapes. There is a similar type, Array. The Screen Fiber-Optic Cables equipped with lenses come with narrower aperture angles for detection in long distances. |
| Narrow-view |
This is a Fiber-Optic Cables that comes with a built-in lens on its head unit for a narrow aperture angle of 2~5˚. In addition to long-distance detection, as these do not get influence from light reflection from a reflective object beside the light axis, these are suitable for use of wafer mapping. 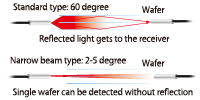
|
Sleeve |
A Fiber-Optic Cables has a thin tube, sleeve, on its head unit. The Sleeve models are suitable to detect a small object in a narrow area. There are Fiber-Optic Cables with bendable sleeves and not-bendable sleeves available. 
|
| Bending resistance |
This is suitable to be installed on a moving part that repeatedly bend a fiber. Their bending radius are r2 and r4 that are larger than those of Flexible fibers. |
Free cut |
A fiber part can be cut by an included fiber cutter. When a Fiber-Optic Cables is too long for an installation distance, an unnecessary part of the fiber can be cut off for easy installation. |
| Coaxial |
This is a kind of diffuse reflective Fiber-Optic Cables that comes with multiple light-receiving cores installed around an emitter core, and is suitable to make detection in higher accuracy. There are Fiber-Optic Cables, which lenses for small object detection can be attached on. 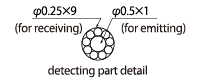
|
Head-on and head-view |
These are Fiber-Optic Cables that detects in a straight direction with optical systems on the top of fiber heads. With the Square units, it is called Head-On, and with the thread and cylindrical units Head-View. 
|
| Through-beam |
Emitter and receiver units are installed on both side, facing each other, and detect an object in between. This makes detection in a long distance possible. 
|
Bending radius |
This is a smallest radius that a Fiber-Optic Cables can be bent. Bending a fiber in a smaller radius may break fiber cores and result in a shorter detection distance or malfunction. 
|
| Thread |
A fiber head is structured with a screw nut for simple installation.
|
Water detection |
This is equipped with a LED with infrared light of 1.45μm wave length. Special Fiber-Optic Sensors, D3IF models, and Fiber-Optic Cables, NF-TW01 and NF-DW01, for water detection are available. Detection of transparent liquid in a transparent glass bottle that was difficult with the conventional sensors can be made. |
| Diffuse reflective |
This is a Fiber-Optic Cables that comes with fibers of light emitter and receiver bundled in a single fiber and detect light reflection from an object. While its detection distance is shorter, a single unit requires less installation work and space. 
|
Lens |
A lens unit is attached on a fiber head. These units are used for long-distance detection and space-saving with through-beam Fiber-Optic Cables and small object detection with diffuse reflective units. There are through-beam Fiber-Optic Cables that come with built-in lenses. |
| Flat-on |
This has detection direction on its side with an optical systems on the large face on a head unit. Thin dimensions to the detection direction of this type make it useful to be installed in a small space in its depth. 
|
Liquid leakage detection |
This fiber head is installed on a leakage pan. With capillary action, this can detect a small amount of liquid or viscous liquid. |
page top 
7. Control output
There are 2 polarities of transistor output, NPN and PNP.
A current flows from the Collector to Emitter on a NPN transistor.
On a PNP transistor, a current flows from the Emitter to Collector.
-
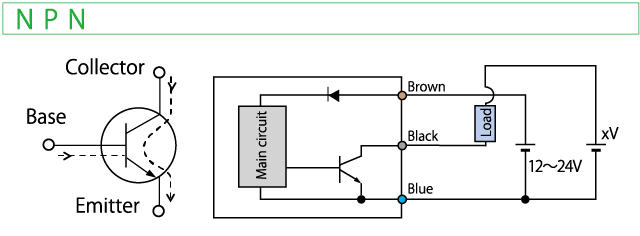
A load to NPN output can be connected to a power supply to the sensor or a separate power supply.
-
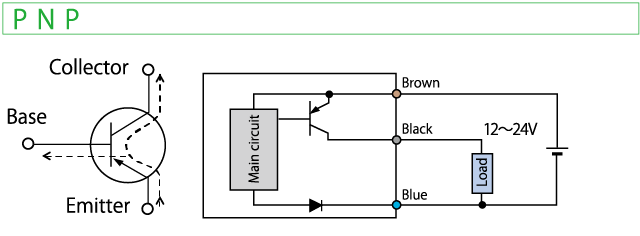
A power supply to load of PNP output must be the same with one to the sensor.
Therefore, a separate power supply with a different voltage from one for the sensor cannot be used.
Voltage output of a transistor
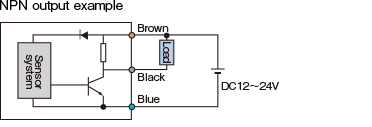
With a NPN transistor, a voltage output flows through a pull-up resistor between a Collector and +V.
Unlike the open collector output, it does not require to connect an external resistor to have a voltage output.
page top 
8. Connection
-
Generally , there are 3 types of connections for sensors, a cable, connector and terminal block, used.
The standard cable length is 2 meters.
For connector connection, M8 4-pin connectors are mainly used, as some sensors has M12 connectors and M12 pigtail cables. -
M8 4-pin connector cables
Straight L-shaped Cable length: 2m M84CN-2S M84CN-2L Cable length: 5m M84CN-5S M84CN-5L Cable length: 10m M84CN-10S M84CN-10L
M12 connector cables
Cable length:2m YF2A14-020VB3XLEAX
(4 pin)YF2A15-020VB5XLEAX
(5 pin)
page top